Data engineering salaries are climbing fast—and it’s not by chance. Companies are collecting more data than ever, but without skilled professionals to organize and manage it, that data is worthless. This demand is reshaping the job market, driving paychecks higher year after year.
In 2025 and beyond, businesses in finance, healthcare, retail, and tech are expected to compete fiercely for top talent. Remote work is also widening opportunities, letting data engineers earn big even outside major tech hubs.
This article breaks down the numbers, the factors driving salaries, and the skills that will keep data engineers among the highest-paid tech professionals in the years ahead.
Average Salary of a Data Engineer in 2025
Entry-Level vs. Mid-Level vs. Senior-Level Salaries
Data engineer salaries in 2025 vary widely based on experience. Entry-level data engineers with less than two years of experience typically earn between $80,000 and $110,000 per year, which works out to roughly $6,700–$9,200 per month or $40–$60 per hour, depending on the company and location.
Mid-level data engineers with three to five years of experience often see salaries climb to $110,000–$160,000 annually, or about $9,200–$13,300 per month. At this stage, most engineers are managing full data pipelines, working with multiple tools, and often contributing to system design.
Senior-level professionals with more than five years of experience, or those in specialized roles like data architects, can earn $160,000 to $250,000 or more. In large tech firms with equity and bonuses, total compensation can easily exceed these numbers, especially in top-paying markets like California, New York, or Washington.
Freelance vs. Full-Time Data Engineer Earnings
Freelance data engineers can sometimes out-earn full-time employees on an hourly basis. Experienced freelancers charge premium rates for specialized skills, and short-term contracts can pay very well. However, income is unpredictable, there are no company-paid benefits, and freelancers must handle their own taxes, tools, and downtime between projects.
Full-time roles, on the other hand, offer stable salaries, health insurance, retirement plans, and potential bonuses or stock options. They also provide structured career growth and training opportunities. For most engineers, full-time positions bring higher overall security, while freelancing appeals to those who value flexibility and are comfortable with the risks and administrative work involved.
Factors That Influence Data Engineer Salaries
Several factors decide whether a data engineer earns on the lower or higher end of the salary range. Understanding these can help professionals plan their careers and employers make better offers.
1. Geographic Location
Location plays a big role in salary differences. Data engineers in tech hubs like San Francisco, New York, and Seattle earn the most because companies there handle massive data systems and face intense competition for talent. However, remote work is changing this—many engineers living in smaller cities are now earning salaries closer to big-city rates as companies hire remotely to access top talent.
2. Skill Set and Certifications
The more in-demand skills you have, the higher your pay. Companies pay premium salaries for data engineers skilled in Python, SQL, Spark, Kafka, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP. Certifications in cloud technologies or big data tools can also boost earnings because they prove expertise in areas companies need most.
3. Company Size and Type
Large companies with massive data infrastructure tend to pay more than smaller businesses. For example, tech giants and financial institutions often pay well above average because they handle sensitive, high-volume data. Startups may pay less in base salary but sometimes offer equity, which can be valuable if the company grows quickly.
4. Education and Academic Background
While many data engineers are self-taught, holding a bachelor’s or master’s degree in computer science, engineering, or data-related fields can open doors to higher-paying roles, especially in competitive industries like finance and healthcare.
5. Experience and Specialized Roles
Salary naturally increases with experience, but specialization can accelerate growth. Roles like big data engineer, data architect, or AI data pipeline engineer often pay more because they require advanced technical skills and deeper knowledge of complex systems.
Data Engineer Salaries by Location
USA: Top-Paying States and Cities
In the United States, data engineer salaries vary significantly by location. States like California, New York, Massachusetts, Washington, and Texas consistently offer some of the highest pay.
Cities such as San Francisco, Seattle, New York City, Boston, and Austin stand out because they host tech giants, finance firms, and growing startups that rely heavily on data infrastructure. Salaries here often cross $150,000 for mid to senior roles, with equity and bonuses pushing total compensation even higher.
However, the cost of living in these cities is high. As remote work gains traction, many companies now pay competitive salaries to engineers living in more affordable states like Colorado, Florida, or North Carolina, narrowing the gap between tech hubs and smaller markets.
Global Salary Comparisons
Outside the US, data engineering remains a well-paying career.
- Canada and Australia offer salaries close to US levels for senior roles, often between $90,000–$140,000 USD equivalent, especially in cities like Toronto, Vancouver, Sydney, and Melbourne.
- European countries like Germany, the UK, and the Netherlands pay competitive wages, with senior roles averaging €70,000–€100,000 annually.
- India and Southeast Asia pay less in absolute terms but offer strong growth potential as local tech ecosystems expand. Senior engineers in India can earn ₹20–35 LPA (roughly $24,000–$42,000 USD), which is high compared to other local IT roles.
Remote-first companies are also creating opportunities for data engineers worldwide to earn salaries closer to US or European standards while living in lower-cost regions, especially for specialized cloud and big data skills.
Salary Growth Potential and Career Pathways
Starter: Where Your Career Can Go
Data engineering offers a clear path from entry-level roles to leadership and specialized positions, with salaries climbing at every step.
Entry-Level: Junior Data Engineer
- Focuses on basic data pipelines, cleaning, and integration tasks.
- Typical salary: $80,000–$110,000 annually.
Mid-Level: Data Engineer / Senior Data Engineer
- Handles complex data systems, works on scaling pipelines, and mentors juniors.
- Typical salary: $110,000–$160,000+ depending on skills and location.
Specialized Roles: Big Data Engineer / Cloud Data Engineer
- Works on real-time data systems, AI pipelines, and cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, or Azure.
- These niche roles often pay $150,000–$ 200,000 or more due to a limited talent supply.
Leadership Roles: Data Architect / Engineering Manager
- Designs entire data architectures or leads engineering teams.
- Salaries often cross $200,000+ with bonuses and equity in large companies.
Future Outlook: 2025 and Beyond
- Demand for real-time analytics, AI infrastructure, and cloud data solutions will keep salaries climbing.
- Career growth opportunities remain strong as businesses collect and rely on more data every year.
Additional Benefits Beyond Base Salary
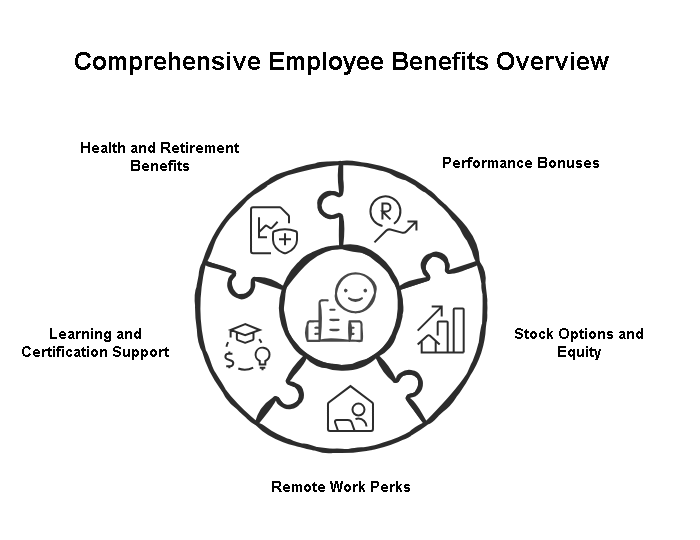
Salary is just part of the package. Many companies offer extras that make a big difference in total compensation. Here are five key benefits:
1. Performance Bonuses
Many employers give annual or quarterly cash bonuses based on company performance or individual goals, adding thousands of dollars on top of your base pay.
2. Stock Options and Equity
Big tech firms and startups often provide equity or stock options. If the company grows, these shares can significantly increase your overall earnings.
3. Remote Work Perks
With remote work now common, some companies pay home office stipends, internet allowances, or coworking space costs, helping you save money while working from anywhere.
4. Learning and Certification Support
Employers often cover online courses, certifications, and conference fees, so you can upgrade your skills without paying out of pocket—and higher skills mean higher future salaries.
5. Health and Retirement Benefits
Standard perks like health insurance, dental plans, paid time off, and retirement contributions add long-term financial value beyond your paycheck.
Tips to Increase Your Salary as a Data Engineer
If you want to move up the pay scale, here are five proven ways to boost your earnings:
1. Master High-Demand Skills
Learning advanced tools like Apache Spark, Kafka, AWS, Azure, or GCP makes you more valuable to employers. Companies pay more for engineers who can manage modern data platforms at scale.
2. Earn Certifications
Certifications like AWS Certified Data Engineer or Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer signal expertise and can open doors to higher-paying roles. Many companies view them as proof of practical skills, not just theory.
3. Gain Experience in Specialized Roles
Roles such as Big Data Engineer, Data Architect, or AI Data Infrastructure Engineer often pay above average because they involve complex systems and niche knowledge.
4. Negotiate and Explore New Offers
Don’t settle for your first offer. Research market rates, highlight your skills, and negotiate. Sometimes, switching companies or moving to a higher-paying industry like finance or tech can result in a big salary jump.
5. Build a Portfolio and Network
Showcasing real projects on GitHub or LinkedIn makes you stand out. Networking at conferences, online forums, or industry events often leads to better opportunities and higher-paying roles.
Conclusion
Data engineering is no longer just a back-end role—it’s becoming the backbone of modern businesses. Salaries are rising not only because companies need data, but because they need reliable systems, real-time analytics, and people who can make sense of massive information flows.
For anyone considering this career, the takeaway is clear: focus on high-demand skills, embrace new technologies like AI and cloud platforms, and stay adaptable as the field keeps growing. Companies will continue paying top dollar for professionals who can turn raw data into actionable insights—and that demand isn’t slowing down anytime soon.
Whether you’re just starting out or aiming for leadership roles, data engineering in 2025 and beyond offers both strong earning potential and long-term career security.




