Cloud data engineers help companies turn massive amounts of information into fast, reliable insights. They build pipelines, manage storage, and use cloud services that keep data flowing without slowing the business down. That’s why demand for skilled cloud data engineers continues to grow.
Interviewers want proof that you can design scalable solutions, write strong SQL, automate workflows, and keep data secure. They also expect clear thinking: how you make decisions, reduce costs, and solve real problems when things break.
This guide covers the exact questions companies ask in cloud data engineering interviews—organized by skill area—so you can practice smarter, show confidence, and stand out as the person they want to hire.
Top Cloud Data Engineer Interview Questions
Cloud data engineer interviews usually start with high-level design questions before diving into tools. These first questions test how you think about storage, pipelines, cost, and trade-offs in cloud systems. If you get this part right, the service-specific questions feel much easier.
Cloud Architecture & Services
1️⃣ What is the difference between data lakes and data warehouses in the cloud?
A data lake stores raw data in many formats for flexible exploration. A data warehouse stores structured, modeled data for fast reporting and dashboards. Interviewers want to see if you understand that lakes are flexible and cheap to store, while warehouses are optimized for performance and business analytics.
2️⃣ How do you select the right cloud storage service for a project?
Object storage fits large files, logs, backups, and analytics data. Block storage fits databases and low-latency workloads. Sometimes, file storage is needed for shared access. Here, they’re checking whether you think about access patterns, latency, durability, and cost instead of picking a service by habit.
3️⃣ Explain how serverless data processing works.
Serverless processing runs your code in short-lived functions without you managing servers. The cloud provider handles scaling and billing based on usage. Interviewers want to hear that you know where it shines—event-driven jobs, bursty workloads—and that you’re aware of limits like execution time and cold starts.
4️⃣ How do you design a scalable and cost-efficient cloud data pipeline?
Use managed services, autoscaling, and clear stages for ingest, process, and load. Minimize data copies, compress where possible, and pick the right storage tier. A strong answer mentions monitoring, alerting, and cost controls, showing you care about reliability and budget at the same time.
5️⃣ What are the pros and cons of managed database services?
Pros: quick setup, automated backups, scaling, patching, and built-in security features.
Cons: less control over hardware and configuration, possible vendor lock-in, and higher cost at large scale. Interviewers want to know whether you can judge whether managed services are worth the trade-offs for a given project.
AWS-Specific Questions
1️⃣ When would you use S3 vs Redshift vs DynamoDB?
S3 stores large files and raw data cheaply for analytics. Redshift is used for fast queries and business reporting. DynamoDB is built for millisecond key-value or document access. Interviewers want to see that you choose services based on performance needs and cost, not assumptions.
2️⃣ Explain the difference between Glue ETL and EMR.
Glue is serverless ETL automation with minimal setup. EMR gives more control for Spark, Hadoop, and big data processing at scale. They’re checking whether you understand when convenience is enough and when you need deeper customization.
3️⃣ How does Kinesis support real-time analytics?
Kinesis streams data and allows consumers to process events instantly for dashboards, monitoring, and alerts. This shows experience with live data, where speed matters more than batch timing.
4️⃣ What security best practices do you apply using IAM, VPC, and encryption?
Grant least-privilege access, isolate sensitive systems in private networks, and encrypt all data. Rotate keys and monitor access to avoid risk. Interviewers want proof that you treat security as part of the build, not something added later.
5️⃣ How do you optimize Redshift performance?
Pick proper sort and distribution keys, compress data, and monitor slow queries. Offload historical data to S3 and use Spectrum to cut costs and reduce scan time. They want someone who improves speed without overspending.
Azure-Specific Questions
1️⃣ Azure Data Lake vs Azure Blob Storage — when to use each?
Azure Data Lake provides analytics-focused features like hierarchical namespaces and finer access control, which help with big data processing. Blob Storage is general-purpose storage for any file type and works well for backups, images, and simple data archiving. Interviewers want to see that you match the service to the workload based on analytics needs and cost.
2️⃣ What role does Azure Data Factory play in ETL/ELT workflows?
Azure Data Factory moves and orchestrates data between services and can trigger transformation jobs. It connects cloud and on-prem systems without a heavy setup. They want to know you understand how data pipelines run across different environments.
3️⃣ Explain Synapse Analytics and its strengths.
Synapse combines SQL analytics, big data processing, and data integration in one workspace. It allows teams to run reporting and large-scale analytics without switching tools. Interviewers look for knowledge of how Synapse simplifies analytics architecture and improves team productivity.
4️⃣ How do you design Cosmos DB for global distribution?
Use multiple write regions, choose a good partition key to spread traffic evenly, and enable local replicas for faster reads. Interviewers want proof that you can reduce latency for users around the world while keeping systems reliable.
5️⃣ What is a managed identity, and how does it enhance security?
Managed identities let services access other Azure resources without storing secrets or keys in code. This reduces risk and simplifies security. They’re checking if you know secure ways to give systems access without exposing credentials.
GCP-Specific Questions
1️⃣ Why is BigQuery cost-efficient for analytical queries?
BigQuery separates storage from compute, so you only pay for the data scanned in each query. It scales automatically and doesn’t require server management. Interviewers want to see that you understand cost control while running large analytics workloads.
2️⃣ When is Dataflow better than Dataproc?
Dataflow is fully managed and ideal for streaming and batch pipelines with automatic scaling. Dataproc gives more control for custom Spark and Hadoop jobs. Interviewers check if you choose tools based on workload automation vs. customization needs.
3️⃣ Explain Pub/Sub and its role in streaming data.
Pub/Sub sends messages between services in real time, allowing systems to react instantly to events. It supports pipelines for logs, clicks, IoT data, and alerts. They want to confirm that you can handle live data flows and design for low-latency processing.
4️⃣ How do you implement IAM to secure pipelines in GCP?
Assign the least access needed, use service accounts for automation, and restrict who can read or write data. Track activity with audit logs. Interviewers look for a practical security approach that reduces mistakes and prevents unauthorized access.
5️⃣ Describe partitioning and clustering options in BigQuery.
Partitioning splits data by date or another key to limit scans. Clustering organizes rows with common values together for faster filtering. They want to know you understand performance tuning and how to lower query cost at the same time.
SQL & Databases
1️⃣ Write a query to find duplicate rows in a table.
You can group rows by the column you want to check and filter where the count is more than one. The idea is simple: if a value appears twice or more, it’s a duplicate. Interviewers want to see you understand the logic behind detecting repeated data, not just syntax.
2️⃣ What’s the difference between OLAP and OLTP systems?
OLTP systems handle quick everyday transactions like placing orders or updating profiles. OLAP systems analyze large historical datasets for trends and reporting. They ask this to confirm you know one supports daily operations, while the other supports business decisions.
3️⃣ How does indexing improve query performance?
Indexes help the database jump straight to the data it needs instead of scanning everything. It’s like using a book’s index instead of flipping every page. Interviewers want to see that you understand speed comes with trade-offs — more indexes slow down inserts and updates.
4️⃣ When would you use partitioning vs sharding?
Partitioning organizes data into smaller segments inside one database to make queries faster. Sharding splits data across multiple servers for scale and availability. They want to know that you can match the approach to the size and load of the system.
5️⃣ Explain the trade-off between ACID and eventual consistency in cloud systems.
ACID ensures everyone sees the same data right away — great for transactions. Eventual consistency allows faster performance at a huge scale, but users may briefly see outdated values. Interviewers check if you understand that cloud systems often choose speed and uptime over perfect synchronization.
Data Modeling & Storage
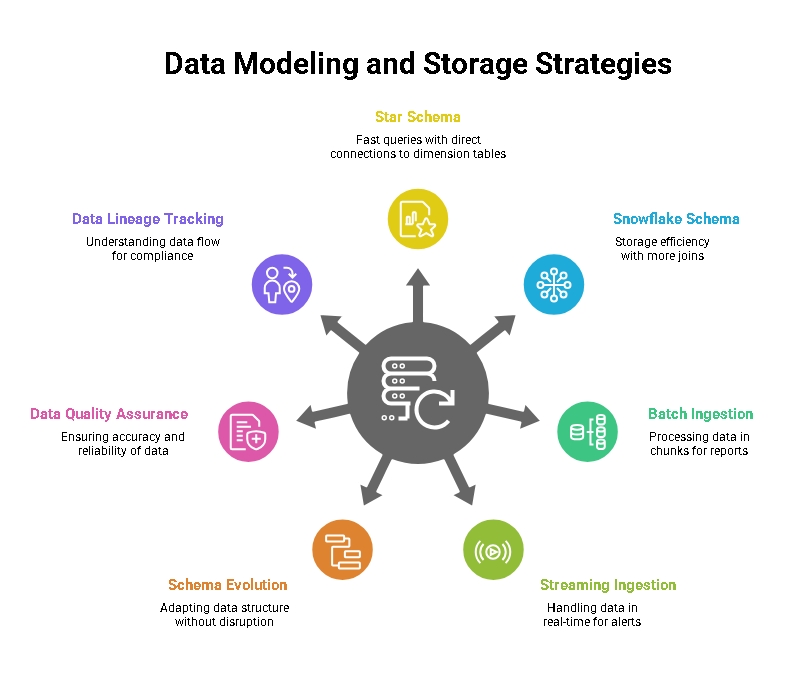
1️⃣ Describe the star schema vs. the snowflake schema.
A star schema has one central fact table with direct connections to dimension tables, making queries fast and simple. A snowflake schema has dimensions broken into more related tables, which saves storage but adds more joins. Interviewers want to see you understand the balance between speed and organization.
2️⃣ Explain batch vs streaming ingestion and when each is needed.
Batch ingestion collects data over time and processes it in chunks, good for daily reports or big transformations. Streaming ingestion handles data as it arrives, used for alerts, fraud detection, or real-time dashboards. They want to know you can match ingestion style with business urgency.
3️⃣ What is schema evolution and why does it matter?
Schema evolution allows changes to data structure — like adding new fields — without breaking pipelines. It keeps systems flexible as data grows and changes. Interviewers want to see you think ahead about long-term maintenance, not just first-day design.
4️⃣ How do you ensure data quality in large pipelines?
Validate data types, handle missing values, remove duplicates, and add checks for accuracy. Monitor pipelines and set alerts so issues are caught early. They’re checking whether you protect the final output, not just move data from A to B.
5️⃣ What is data lineage, and how do you track it?
Data lineage shows where data came from, how it was processed, and where it goes. It helps with debugging, trust, compliance, and auditing. Interviewers want someone who can explain how data flows — because clarity prevents mistakes.
DevOps, CI/CD & Automation
1️⃣ What is Infrastructure as Code and what tools have you used?
Infrastructure as Code means defining servers, networks, and services using configuration files instead of manual setup. Tools like Terraform, CloudFormation, or Bicep help automate and repeat those deployments. Interviewers want to see that you avoid “clicking around” and build systems that can be recreated easily.
2️⃣ How do you implement CI/CD for data pipelines?
Store pipeline code in version control, run automated tests, and deploy changes through a controlled workflow. Use tools like GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, or AWS CodePipeline. They’re checking that you release updates safely without breaking production data.
3️⃣ What metrics do you monitor for pipeline performance?
Track data freshness, throughput, failure rates, and processing time. Also, monitor costs so jobs don’t grow out of budget. Interviewers want someone who doesn’t set a pipeline and forget it — you keep it healthy and efficient.
4️⃣ Explain container orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes) in data workflows.
Kubernetes schedules and scales containers so data jobs can run reliably even when demand changes. It helps manage resources and avoid downtime. They ask this to see if you understand running data services in a flexible, cloud-friendly way.
5️⃣ How do you handle versioning for ETL/ELT transformations?
Version control for code, clear tracking of schema changes, and tagging releases for rollback if something breaks. Interviewers want confidence that you protect data and always know what changed and why
Security & Compliance
1️⃣ How do you secure data at rest and in transit in the cloud?
Encrypt stored data using keys managed by the cloud provider or a dedicated key service. Use HTTPS/TLS to secure data while moving between systems. Interviewers want to see that security is a part of your design, not an afterthought.
2️⃣ What is the principle of least privilege?
Give users and systems only the access they need to do their job — nothing more. This reduces exposure if credentials are misused. They’re checking if you prevent risks instead of reacting later.
3️⃣ What steps do you take to handle PII/PHI securely?
Mask or anonymize sensitive fields, limit access to authorized roles, encrypt storage and transfers, and log activity for compliance. Interviewers want someone who understands privacy laws and treats personal data with care.
4️⃣ How do you audit and monitor access in cloud systems?
Enable auditing tools to track who accessed what, set alerts for unusual activity, and review logs routinely. They want to know you watch for problems before customers notice anything wrong.
5️⃣ Explain tokenization vs encryption in data privacy.
Encryption scrambles data into an unreadable form and requires a key to unlock. Tokenization replaces the data with a placeholder token while keeping the real value stored securely elsewhere. Interviewers want to see that you know different ways to protect data based on risk and performance needs.
Behavioral / Communication
1️⃣ Describe a time your pipeline failed. What did you do?
Share a real issue, like data arriving late or a job breaking after a schema change. Explain how you diagnosed the cause, fixed it, and prevented it from happening again. Interviewers want proof that you stay calm under pressure and learn from failures instead of blaming others.
2️⃣ How do you prioritize tasks when stakeholders disagree?
Show that you listen to everyone, define the actual business goals, and choose the work that creates the most value or reduces the biggest risk. They want to see you communicate clearly, not just take orders from the loudest voice.
3️⃣ Tell us about a project where you reduced cost or improved performance.
Pick a measurable win — faster pipeline runs, fewer compute resources, or a cheaper storage strategy. Mention the impact, like saving time for analysts or cutting cloud bills. They want someone who thinks like an owner, not just a builder.
4️⃣ What’s the biggest data engineering challenge you’ve solved?
Describe a situation that required teamwork, debugging, or redesigning part of the system. Explain the challenge, what you did, and the lesson you carried forward. They’re checking for creativity and resilience.
5️⃣ How do you keep yourself updated on new cloud technologies?
Mention practical learning habits like hands-on labs, certification study, cloud blogs, or joining community groups. They want someone who stays current because cloud tools change fast.
Skills Interviewers Expect You to Demonstrate
Interviewers aren’t just checking if you know cloud services; they’re looking for a few core skills that show you can handle real projects and real problems.
- Cloud-first mindset
You think in terms of managed services, scaling, and cost from day one. Instead of spinning up random servers, you pick services that handle growth and reduce manual work. You can build this skill by rebuilding a small project using serverless tools or managed databases and then reviewing the cloud bill to see how design choices change cost. - Data pipeline and ecosystem understanding
You know how data moves from source systems into storage, through transformation, and finally into analytics tools. You see how streaming, batch, storage, and permissions all connect. To grow here, practice building small end-to-end pipelines that pull data from APIs or files, process it, and land it in a warehouse or lake that analysts can use. - SQL and data modeling
You write clear queries and shape data so teams can answer questions quickly. Instead of dumping tables, you think about structure, filters, and performance. You can sharpen this by taking a messy dataset, reorganizing it into a cleaner model, and comparing how much easier it is to query and report on. - Troubleshooting and ownership
You don’t panic when a pipeline fails; you diagnose, fix, and learn from it. You take responsibility for data quality and reliability instead of assuming “it’s someone else’s problem.” A great way to build this is to break a test pipeline on purpose—change a schema, slow a service, or remove a file—then practice tracking down the issue and documenting the fix. - Communication with non-technical teams
You can explain designs and trade-offs in simple language so that product, analytics, and leadership understand what’s happening and why it matters. Instead of diving straight into services and specs, you link your choices to outcomes like lower cost, faster reporting, or less risk. You can improve this by practicing short explanations of your projects to a friend or colleague who isn’t deep into engineering.
Conclusion
Cloud data engineering interviews are easier to handle when you focus on real skills instead of memorizing answers. Build something small in each cloud platform, break it on purpose, then fix it — that’s how confidence is built. Practice explaining your design choices to someone who isn’t technical, because the best engineers can make others smarter, too. Finally, bring stories from real experiences — even small wins show that you solve problems, learn fast, and take ownership. If you walk into the interview with that mindset, you’re already ahead of most candidates.




